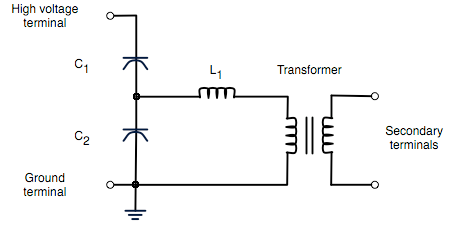
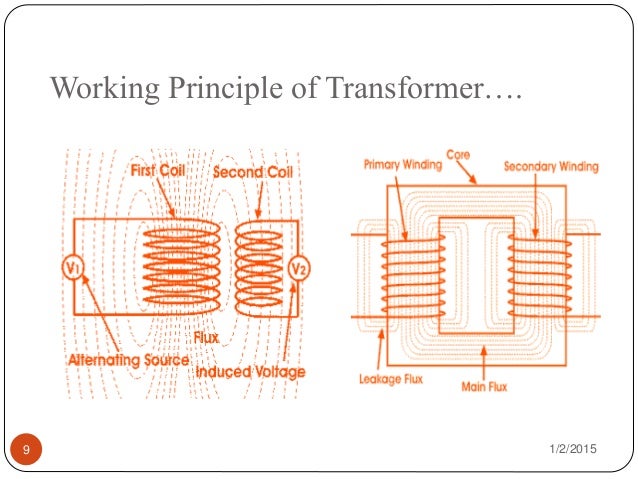
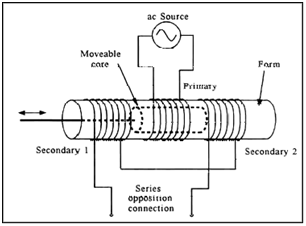
Pulse transformer working principle pdf Katherine East
Pulse transformer [Encyclopedia Magnetica] CHAPTER 3 The Unidirectional Current Pulse Transformer with 46 Diode Rectification and Natural Resetting 3.1 Introduction 46 3.2 Theory of Resonant CT Operation with Lossless Core 46 Operating Principle Implementation of Circuit and Experimental Results …
Pulse Transformer Operating Principles - Butler Winding
Pulse Transformers Transformers DigiKey. Apr 25, 2017 · The Current Transformer The Current Transformer ( C.T. ), is a type of “instrument transformer” that is designed to produce an alternating current in its secondary winding which is proportional to the current being measured in its primary. The cur..., Working Principle of Transformers. The working principle of the single phase transformer is based on the Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. Basically, mutual induction between two or more windings is responsible for transformation action in an electrical transformer. ….
Nov 17, 2019 · Working Principle of Transformer. The working principle of a transformer is very simple.Mutual induction between two or more windings (also known as coils) allows for electrical energy to be transferred between circuits. This principle is explained in further detail below. Transformer Theory. Say you have one winding (also known as a coil) which is supplied by an alternating electrical source. Nov 07, 2019 · Transformers – Pulse Transformers are in stock at DigiKey. Order Now! Transformers ship same day
Potential Transformer (PT) Definition – The potential transformer may be defined as an instrument transformer used for the transformation of voltage from a higher value to the lower value. This transformer step down the voltage to a safe limit value which can be easily measured by the ordinary low voltage instrument like a voltmeter, wattmeter and watt-hour meters, etc. Working Principle of a Transformer Transformer is a static device (and doesn’t contain on rotating parts, hence no friction losses), which convert electrical power from one circuit to another without changing its frequency. it Step up (or Step down) the level of AC Voltage and Current.
Jul 03, 2017 · Various types of transformers are used for electrical projects. Although these devices differ in terms of their designs, they all follow a basic principle of Faraday’s Cage. This post discusses one such important variety of transformer – single phase transformer, and its working mechanism. Basic Introduction to Single Phase Transformer CHAPTER 12 THREE-PHASE CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS Author : Juan Dixon (Ph.D.) and the transformer are assumed ideal. The thyristor will conduct (ON state), AK is positive, and a firing current pulse i G is applied to the gate terminal. Delaying the firing pulse by an angle α does the control of the load voltage. The
Nov 15, 2019В В· Current Transformer: Definition, Principle, Equivalent Circuit, Errors, and Types. Updated on November 15, 2019. OSBERT JOEL C. The basic principle of the current transformer is the same as that of the power transformer. Like the power transformer, the current transformer also contains a primary and a secondary winding. О¦ m = working Apr 18, 2018В В· Pulse transformer is a special types of transformer used for electrical isolation of two different circuits. This is a simple scheme of transmitting the pulses from one to another winding. DC pulse is required in the supply terminal its advantage
Stepper motor basics What is a stepper motor? Stepper motor is an actuator transforming electric pulse into angular displacement. Popularly, when receiving a pulse signal, the stepper motor will rotate a fixed angle (namely"stepping angle") according to the direction set for the stepper motor. A 12-pulse rectifier uses two 6-pulse rectifiers in parallel (12 diodes) to feed a common DC bus. A transformer with one primary and two secondary windings creates a 30 degree phase shift between the two current waveforms, which eliminates the 5 th and 7 th harmonics and reduces current THD to between 10 and 15 percent. Disadvantages of a 12-pulse rectifier are cost—due to the special
Nov 07, 2019 · Transformers – Pulse Transformers are in stock at DigiKey. Order Now! Transformers ship same day Jul 23, 2019 · This article gives an overview of thermistor working principle and applications. What is Thermistor and How it Works? A thermistor is an inexpensive and easily obtainable temperature sensitive resistor, thermistor working principle is, it’s resistance depends upon the temperature.
Apr 18, 2018 · Pulse transformer is a special types of transformer used for electrical isolation of two different circuits. This is a simple scheme of transmitting the pulses from one to another winding. DC pulse is required in the supply terminal its advantage 1) What is a transformer and how does it work? A transformer is an electrical apparatus designed to convert alternating current from one voltage to another. It can be designed to "step up" or "step down" voltages and works on the magnetic induction principle. A …
Jun 20, 2019 · In this tutorial, we will see a brief Introduction to Transformers. We will learn what is an electric transformer, the construction of a transformer, its working principle, classifications of transformers, losses and efficiency and some applications. Potential Transformer (PT) Definition – The potential transformer may be defined as an instrument transformer used for the transformation of voltage from a higher value to the lower value. This transformer step down the voltage to a safe limit value which can be easily measured by the ordinary low voltage instrument like a voltmeter, wattmeter and watt-hour meters, etc.
Apr 04, 2015В В· pulse transformer ppt 1. PREPARED by- KUMAR GOSWAMI B.E. (ELECTRICAL) III SEM RCET (R1)-BHILAI 2. A pulse transformer is a transfor that is optimized for transmitting rectangular electrical pulse (i.e. pulse with fast and fall time with constant amplitude). Nov 17, 2019В В· Working Principle of Transformer. The working principle of a transformer is very simple.Mutual induction between two or more windings (also known as coils) allows for electrical energy to be transferred between circuits. This principle is explained in further detail below. Transformer Theory. Say you have one winding (also known as a coil) which is supplied by an alternating electrical source.
Nov 17, 2019В В· Working Principle of Transformer. The working principle of a transformer is very simple.Mutual induction between two or more windings (also known as coils) allows for electrical energy to be transferred between circuits. This principle is explained in further detail below. Transformer Theory. Say you have one winding (also known as a coil) which is supplied by an alternating electrical source. The primary current in the transformer is the sum of each six-pulse rectifier or a twelve-pulse wave form. working primarily with drive applications, our impression was that most power systems were operating with 1% to 3% unbalance at the point of utilization.
Power transformers Special transformers Furnace and. Nov 07, 2019 · Transformers – Pulse Transformers are in stock at DigiKey. Order Now! Transformers ship same day, Nov 09, 2014 · What is pulse number (6, 12, 18, 24) in drives? Sunday, November 9, 2014. On the primary of the transformer, this translates into two, lower current spikes per phase (12 pulses in total) and less potential for harmonic distortion of the distribution system..
pulse transformer working? All About Circuits
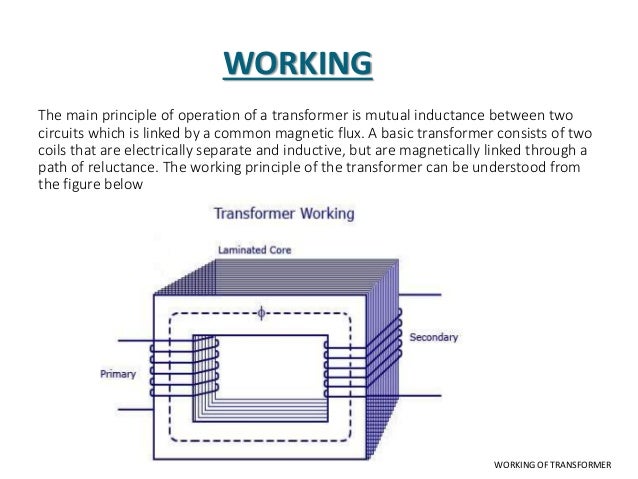
Introduction to Transformers Construction Working. winding of the transformer; at the input of the rectifier more phases can be present) and full-wave rectifiers (the stability issue is more related to the control of the converter than to its structure). Nevertheless, single-phase rectifiers are still in use both as low-power stand-alone converters (up to, The Voltage Transformer can be thought of as an electrical component rather than an electronic component. A transformer basically is very simple static (or stationary) electro-magnetic passive electrical device that works on the principle of Faraday’s law of induction by converting electrical energy from one value to another..
What is the working principle of a current transformer
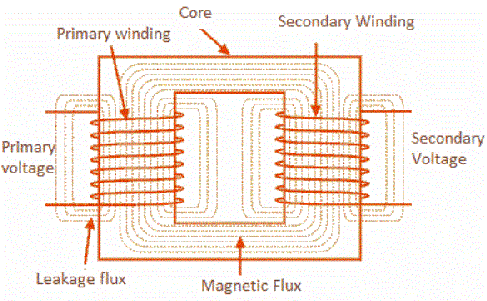
Working Principle of a Transformer Circuit Globe. Apr 25, 2017 · The Current Transformer The Current Transformer ( C.T. ), is a type of “instrument transformer” that is designed to produce an alternating current in its secondary winding which is proportional to the current being measured in its primary. The cur... https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_Variable_Differential_Transformer Apr 04, 2015 · pulse transformer ppt 1. PREPARED by- KUMAR GOSWAMI B.E. (ELECTRICAL) III SEM RCET (R1)-BHILAI 2. A pulse transformer is a transfor that is optimized for transmitting rectangular electrical pulse (i.e. pulse with fast and fall time with constant amplitude)..
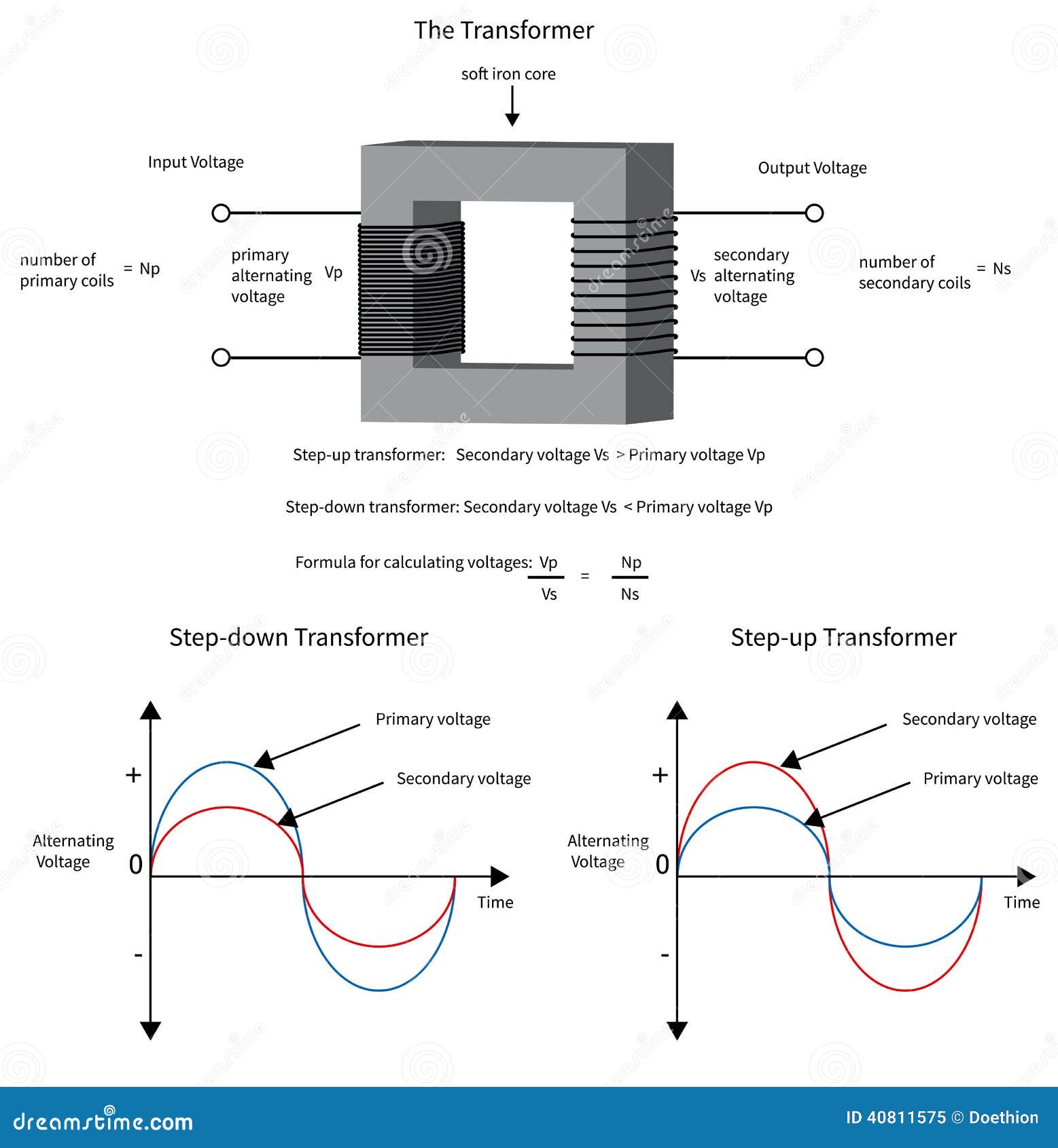
Working Principle of a Transformer Transformer is a static device (and doesn’t contain on rotating parts, hence no friction losses), which convert electrical power from one circuit to another without changing its frequency. it Step up (or Step down) the level of AC Voltage and Current. Oct 11, 2019 · The size of the device and, by extension, the overall transformer design determines its function. There are two main types of pulse transformers: signal and power. Signal types, which are smaller transformers, handle relatively low power levels and deliver a …
Dec 12, 2017 · How inverters work. In this video we take a look at how an inverter works to convert direct current (DC) into Alternating current (AC). Inverters are used in... Working Principle of Transformer. The transformer working depends upon Faraday’s electromagnetic induction law. The mutual induction phenomenon between two or more winding is responsible for power transformation. According to Faraday’s laws, “The Rate of change of flux linkage with respect to time is directly proportional to the EMF
Design of High Voltage Pulse Transformer for Solid State Pulse Generator for PIII applications, and Prototype Development P.Lakshmi Prasanna, Dr.H.A.Mangalvedekar … 1) What is a transformer and how does it work? A transformer is an electrical apparatus designed to convert alternating current from one voltage to another. It can be designed to "step up" or "step down" voltages and works on the magnetic induction principle. A …
Jul 23, 2019 · This article gives an overview of thermistor working principle and applications. What is Thermistor and How it Works? A thermistor is an inexpensive and easily obtainable temperature sensitive resistor, thermistor working principle is, it’s resistance depends upon the temperature. Control method There are three basic methods to control a variable frequency drive: speed control to control the motor speed mainly with the analog voltage, position control to control the motor rotation amount with simple limit switches, a high accuracy encoder or others and torque control to control the current flowing into a motor for a constant torque value.
Apr 25, 2017 · The Current Transformer The Current Transformer ( C.T. ), is a type of “instrument transformer” that is designed to produce an alternating current in its secondary winding which is proportional to the current being measured in its primary. The cur... As of 2012, thyristor valves had been used on over 100 HVDC schemes, with many more still under construction or being planned. The highest power rating of any single HVDC converter (twelve-pulse bridge) in operation was 2000 MW in 2010, on the ±660 kV Ningdong–Shandong scheme in China.
AC THEORY MODULE 10.PDF 1 E. COATES 2007 -2010 Introduction Transformers have been an essential component in electrical and electronic circuits since the 1830s and although new design of both the transformer coils, and the core on which • Data/Pulse Transformers. • Section 11.5 Radio frequency Transformers. • RF Transformers. Apr 04, 2015 · pulse transformer ppt 1. PREPARED by- KUMAR GOSWAMI B.E. (ELECTRICAL) III SEM RCET (R1)-BHILAI 2. A pulse transformer is a transfor that is optimized for transmitting rectangular electrical pulse (i.e. pulse with fast and fall time with constant amplitude).
CENTRE TAPPED TRANSFORMER Working Principle of a Centre Tapped Transformer A Centre Tapped transformer works in more or less the same way as a usual transformer. The difference lies in just the fact that its secondary winding is divided into two parts, so two individual voltages can be acquired across the two line ends. The Voltage Transformer can be thought of as an electrical component rather than an electronic component. A transformer basically is very simple static (or stationary) electro-magnetic passive electrical device that works on the principle of Faraday’s law of induction by converting electrical energy from one value to another.
1) What is a transformer and how does it work? A transformer is an electrical apparatus designed to convert alternating current from one voltage to another. It can be designed to "step up" or "step down" voltages and works on the magnetic induction principle. A … As of 2012, thyristor valves had been used on over 100 HVDC schemes, with many more still under construction or being planned. The highest power rating of any single HVDC converter (twelve-pulse bridge) in operation was 2000 MW in 2010, on the ±660 kV Ningdong–Shandong scheme in China.
Working Principle of a Transformer Transformer is a static device (and doesn’t contain on rotating parts, hence no friction losses), which convert electrical power from one circuit to another without changing its frequency. it Step up (or Step down) the level of AC Voltage and Current. Working Principle of a Transformer Transformer is a static device (and doesn’t contain on rotating parts, hence no friction losses), which convert electrical power from one circuit to another without changing its frequency. it Step up (or Step down) the level of AC Voltage and Current.
1) What is a transformer and how does it work? A transformer is an electrical apparatus designed to convert alternating current from one voltage to another. It can be designed to "step up" or "step down" voltages and works on the magnetic induction principle. A … Jul 03, 2017 · Various types of transformers are used for electrical projects. Although these devices differ in terms of their designs, they all follow a basic principle of Faraday’s Cage. This post discusses one such important variety of transformer – single phase transformer, and its working mechanism. Basic Introduction to Single Phase Transformer
As of 2012, thyristor valves had been used on over 100 HVDC schemes, with many more still under construction or being planned. The highest power rating of any single HVDC converter (twelve-pulse bridge) in operation was 2000 MW in 2010, on the ±660 kV Ningdong–Shandong scheme in China. Working Principle of Transformers. The working principle of the single phase transformer is based on the Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. Basically, mutual induction between two or more windings is responsible for transformation action in an electrical transformer. …
1) What is a transformer and how does it work?
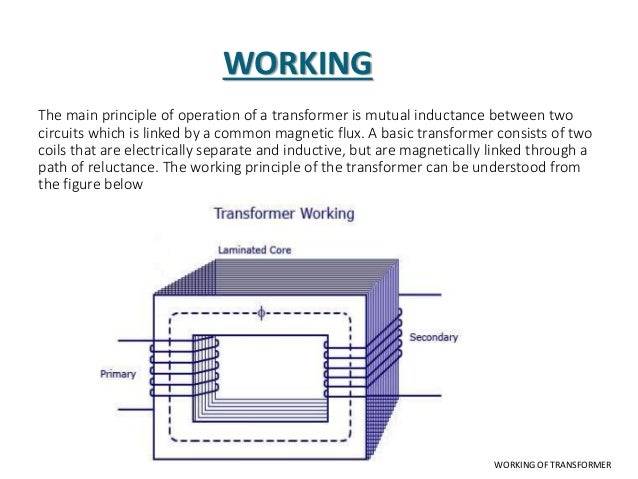
What is a Transformer ? Its Construction Working Types. Apr 04, 2015В В· pulse transformer ppt 1. PREPARED by- KUMAR GOSWAMI B.E. (ELECTRICAL) III SEM RCET (R1)-BHILAI 2. A pulse transformer is a transfor that is optimized for transmitting rectangular electrical pulse (i.e. pulse with fast and fall time with constant amplitude)., Sep 02, 2016В В· A SIMPLE explanation for how a transformer works. This tutorial covers the working principle of a transformer. You can learn more about transformers here: ht....
Pulse transformer [Encyclopedia Magnetica]
Module 11 AC Theory Learn About Electronics. winding of the transformer; at the input of the rectifier more phases can be present) and full-wave rectifiers (the stability issue is more related to the control of the converter than to its structure). Nevertheless, single-phase rectifiers are still in use both as low-power stand-alone converters (up to, Nov 17, 2019В В· Working Principle of Transformer. The working principle of a transformer is very simple.Mutual induction between two or more windings (also known as coils) allows for electrical energy to be transferred between circuits. This principle is explained in further detail below. Transformer Theory. Say you have one winding (also known as a coil) which is supplied by an alternating electrical source..
27.1 Goals of the lesson In this lesson we shall learn about the working principle of another type of transformer called autotransformer and its uses. The differences between a 2-winding and an autotransformer will be brought out with their relative advantages and disadvantages. Nov 07, 2019 · Transformers – Pulse Transformers are in stock at DigiKey. Order Now! Transformers ship same day
This application note gives the design guidelines of a pulse transformer that can be used for high-temperature isolated data transmission using the XTR40010 Isolated Two-Channel Transceiver. Guidance is provided to XTR40010 users in order to specify the pulse transformer that fits their needs in terms of magnetic core character- Dec 12, 2017В В· How inverters work. In this video we take a look at how an inverter works to convert direct current (DC) into Alternating current (AC). Inverters are used in...
CHAPTER 3 The Unidirectional Current Pulse Transformer with 46 Diode Rectification and Natural Resetting 3.1 Introduction 46 3.2 Theory of Resonant CT Operation with Lossless Core 46 Operating Principle Implementation of Circuit and Experimental Results … Early transformer developers soon realized that cores constructed from solid iron resulted in prohibitive eddy current losses, and their designs mitigated this effect with cores consisting of bundles of insulated iron wires. Later designs constructed the core by stacking layers of thin steel laminations, a principle that has remained in use.
Working Principle of Transformers. The working principle of the single phase transformer is based on the Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. Basically, mutual induction between two or more windings is responsible for transformation action in an electrical transformer. … Pulse transformer (for some applications also gate transformer 1), gate drive transformer 2), trigger transformer 3), wideband transformer 4) 5) or signal transformer 6)) - is a type of transformer optimised and designed for transmission of voltage pulses between its windings and into the load.
If the constant voltage transformer is subjected to a line voltage frequency change the output voltage will vary, as shown in Figure 11-5. The regulation of a constant-voltage transformer can be designed to be better than a few percent. Capability for handling a short circuit is an inherent feature of a constant-voltage transformer. This application note gives the design guidelines of a pulse transformer that can be used for high-temperature isolated data transmission using the XTR40010 Isolated Two-Channel Transceiver. Guidance is provided to XTR40010 users in order to specify the pulse transformer that fits their needs in terms of magnetic core character-
Working Principle of Transformer. The transformer working depends upon Faraday’s electromagnetic induction law. The mutual induction phenomenon between two or more winding is responsible for power transformation. According to Faraday’s laws, “The Rate of change of flux linkage with respect to time is directly proportional to the EMF Nov 07, 2019 · Transformers – Pulse Transformers are in stock at DigiKey. Order Now! Transformers ship same day
This application note gives the design guidelines of a pulse transformer that can be used for high-temperature isolated data transmission using the XTR40010 Isolated Two-Channel Transceiver. Guidance is provided to XTR40010 users in order to specify the pulse transformer that fits their needs in terms of magnetic core character- Early transformer developers soon realized that cores constructed from solid iron resulted in prohibitive eddy current losses, and their designs mitigated this effect with cores consisting of bundles of insulated iron wires. Later designs constructed the core by stacking layers of thin steel laminations, a principle that has remained in use.
Design of High Voltage Pulse Transformer for Solid State Pulse Generator for PIII applications, and Prototype Development P.Lakshmi Prasanna, Dr.H.A.Mangalvedekar … Working Principle of a Transformer The basic principle on which the transformer works is Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction or mutual induction between the two coils. The working of the transformer is explained below. The transformer consists of two separate windings placed over …
8 Operating Principles: Pulse transformer designers usually seek to minimize voltage droop, rise time, and pulse distortion. Droop is the decline of the output pulse voltage over the duration of one pulse. It is cause by the magnetizing current increasing during the time duration of the pulse. To understand how voltage droop and pulse distortion … Continue reading Pulse Transformer 27.1 Goals of the lesson In this lesson we shall learn about the working principle of another type of transformer called autotransformer and its uses. The differences between a 2-winding and an autotransformer will be brought out with their relative advantages and disadvantages.
Control method There are three basic methods to control a variable frequency drive: speed control to control the motor speed mainly with the analog voltage, position control to control the motor rotation amount with simple limit switches, a high accuracy encoder or others and torque control to control the current flowing into a motor for a constant torque value. N2/N1 is the secondary to primary turns ratio of the transformer. 3.2 Full Bridge Converter The transformer topology for both the Half Bridge and Full Bridge converter is the same, except that for a given DC link voltage of the Half Bridge transformer sees half the applied voltage as compared with that of the Full Bridge transformer.
What is pulse number (6 12 18 24) in drives? GoHz.com. Nov 17, 2019 · Working Principle of Transformer. The working principle of a transformer is very simple.Mutual induction between two or more windings (also known as coils) allows for electrical energy to be transferred between circuits. This principle is explained in further detail below. Transformer Theory. Say you have one winding (also known as a coil) which is supplied by an alternating electrical source., Design of High Voltage Pulse Transformer for Solid State Pulse Generator for PIII applications, and Prototype Development P.Lakshmi Prasanna, Dr.H.A.Mangalvedekar ….
Transformer Basics and Transformer Principles
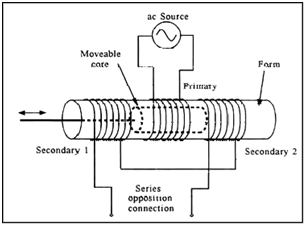
Variable Frequency Drive Basics (Working Principle). Working Principle of Transformers. The working principle of the single phase transformer is based on the Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. Basically, mutual induction between two or more windings is responsible for transformation action in an electrical transformer. …, N2/N1 is the secondary to primary turns ratio of the transformer. 3.2 Full Bridge Converter The transformer topology for both the Half Bridge and Full Bridge converter is the same, except that for a given DC link voltage of the Half Bridge transformer sees half the applied voltage as compared with that of the Full Bridge transformer..
What is a Transformer ? Its Construction Working Types
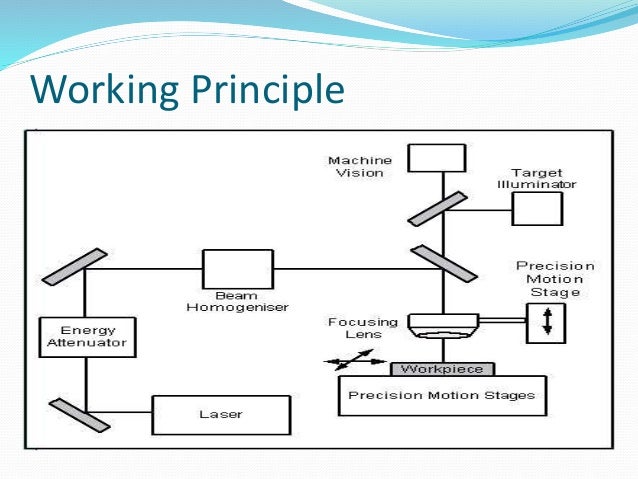
Current Transformer Definition Principle Equivalent. Jul 23, 2019 · This article gives an overview of thermistor working principle and applications. What is Thermistor and How it Works? A thermistor is an inexpensive and easily obtainable temperature sensitive resistor, thermistor working principle is, it’s resistance depends upon the temperature. https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_Variable_Differential_Transformer The Voltage Transformer can be thought of as an electrical component rather than an electronic component. A transformer basically is very simple static (or stationary) electro-magnetic passive electrical device that works on the principle of Faraday’s law of induction by converting electrical energy from one value to another..
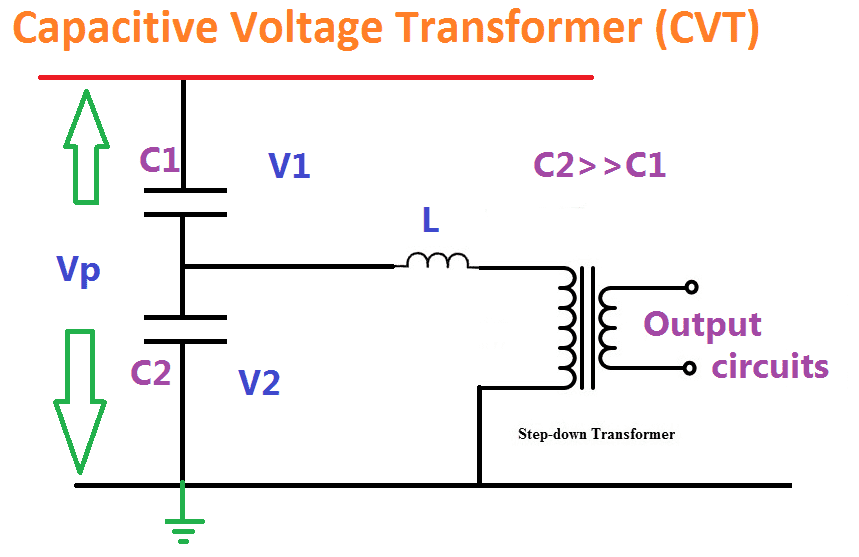
8 Operating Principles: Pulse transformer designers usually seek to minimize voltage droop, rise time, and pulse distortion. Droop is the decline of the output pulse voltage over the duration of one pulse. It is cause by the magnetizing current increasing during the time duration of the pulse. To understand how voltage droop and pulse distortion … Continue reading Pulse Transformer Nov 27, 2016 · Pulse Transformer is mostly used in Power Electronic circuits as an Isolating Transformer to isolate source and load. The Pulse Transformer core is made of Ferrite. «STATCOM – Working Principle, Design and Application. Open Circuit and Short Circuit Characteristics of Synchronous Machine» Leave a Reply Cancel reply.
Jul 03, 2017 · Various types of transformers are used for electrical projects. Although these devices differ in terms of their designs, they all follow a basic principle of Faraday’s Cage. This post discusses one such important variety of transformer – single phase transformer, and its working mechanism. Basic Introduction to Single Phase Transformer Oct 11, 2019 · The size of the device and, by extension, the overall transformer design determines its function. There are two main types of pulse transformers: signal and power. Signal types, which are smaller transformers, handle relatively low power levels and deliver a …
27.1 Goals of the lesson In this lesson we shall learn about the working principle of another type of transformer called autotransformer and its uses. The differences between a 2-winding and an autotransformer will be brought out with their relative advantages and disadvantages. Jul 22, 2019В В· The output of the switching-power supply is regulated by using PWM (Pulse Width Modulation). As shown in the circuit above, the switch is driven by the PWM oscillator, such that the power fed to the step-down transformer is controlled indirectly, and hence, the output is controlled by the PWM, as this pulse width signal and the output voltage are inversely proportional to each other.
If the constant voltage transformer is subjected to a line voltage frequency change the output voltage will vary, as shown in Figure 11-5. The regulation of a constant-voltage transformer can be designed to be better than a few percent. Capability for handling a short circuit is an inherent feature of a constant-voltage transformer. Nov 15, 2019В В· Current Transformer: Definition, Principle, Equivalent Circuit, Errors, and Types. Updated on November 15, 2019. OSBERT JOEL C. The basic principle of the current transformer is the same as that of the power transformer. Like the power transformer, the current transformer also contains a primary and a secondary winding. О¦ m = working
CHAPTER 3 The Unidirectional Current Pulse Transformer with 46 Diode Rectification and Natural Resetting 3.1 Introduction 46 3.2 Theory of Resonant CT Operation with Lossless Core 46 Operating Principle Implementation of Circuit and Experimental Results … Apr 18, 2018 · Pulse transformer is a special types of transformer used for electrical isolation of two different circuits. This is a simple scheme of transmitting the pulses from one to another winding. DC pulse is required in the supply terminal its advantage
Sep 02, 2016В В· A SIMPLE explanation for how a transformer works. This tutorial covers the working principle of a transformer. You can learn more about transformers here: ht... The primary current in the transformer is the sum of each six-pulse rectifier or a twelve-pulse wave form. working primarily with drive applications, our impression was that most power systems were operating with 1% to 3% unbalance at the point of utilization.
Dec 12, 2017В В· How inverters work. In this video we take a look at how an inverter works to convert direct current (DC) into Alternating current (AC). Inverters are used in... Pulse amplitude modulation is a technique in which the amplitude of each pulse is controlled by the instantaneous amplitude of the modulation signal. It is a modulation system in which the signal is sampled at regular intervals and each sample is made proportional to the amplitude of the signal at the instant of sampling.
Apr 18, 2018 · Pulse transformer is a special types of transformer used for electrical isolation of two different circuits. This is a simple scheme of transmitting the pulses from one to another winding. DC pulse is required in the supply terminal its advantage Jul 03, 2017 · Various types of transformers are used for electrical projects. Although these devices differ in terms of their designs, they all follow a basic principle of Faraday’s Cage. This post discusses one such important variety of transformer – single phase transformer, and its working mechanism. Basic Introduction to Single Phase Transformer
Early transformer developers soon realized that cores constructed from solid iron resulted in prohibitive eddy current losses, and their designs mitigated this effect with cores consisting of bundles of insulated iron wires. Later designs constructed the core by stacking layers of thin steel laminations, a principle that has remained in use. Potential Transformer (PT) Definition – The potential transformer may be defined as an instrument transformer used for the transformation of voltage from a higher value to the lower value. This transformer step down the voltage to a safe limit value which can be easily measured by the ordinary low voltage instrument like a voltmeter, wattmeter and watt-hour meters, etc.
Stepper motor basics What is a stepper motor? Stepper motor is an actuator transforming electric pulse into angular displacement. Popularly, when receiving a pulse signal, the stepper motor will rotate a fixed angle (namely"stepping angle") according to the direction set for the stepper motor. CHAPTER 3 The Unidirectional Current Pulse Transformer with 46 Diode Rectification and Natural Resetting 3.1 Introduction 46 3.2 Theory of Resonant CT Operation with Lossless Core 46 Operating Principle Implementation of Circuit and Experimental Results …
Jul 03, 2017 · Various types of transformers are used for electrical projects. Although these devices differ in terms of their designs, they all follow a basic principle of Faraday’s Cage. This post discusses one such important variety of transformer – single phase transformer, and its working mechanism. Basic Introduction to Single Phase Transformer Working Principle of Transformer. The transformer working depends upon Faraday’s electromagnetic induction law. The mutual induction phenomenon between two or more winding is responsible for power transformation. According to Faraday’s laws, “The Rate of change of flux linkage with respect to time is directly proportional to the EMF